Studies show vaccines protect against serious Omicron illness
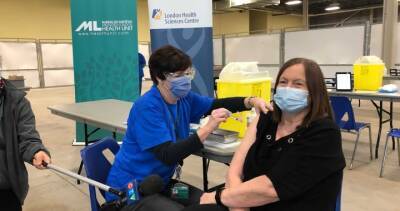
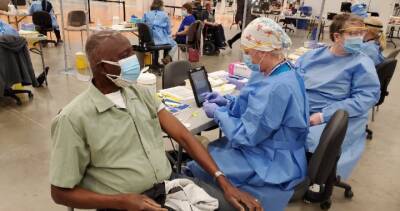
A pair of new studies that sized up how COVID-19 vaccines affected hospitalizations, including during the Omicron variant surge, found that mRNA vaccines were highly effective against severe illness and that unvaccinated people were 12 times more likely to be hospitalized compared with those who had received a booster, with the risk especially high in Black patients.In other COVID-19 developments, Moderna yesterday file for approval for emergency use for fourth doses of its mRNA vaccine as surges in Asian hot spots continued at very high levels.Vaccines, boosters crucial toolThe authors of both studies assessed how well vaccination protected against hospitalization during the worst of the Omicron surge and compared it with how well the vaccines held up during the Delta surge.
Both studies were published today in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR).The first study examined how mRNA vaccines protected against the most severe outcomes, defined as ventilator treatment or death.
The authors looked for any differences between patients who had gotten their primary series and those who had also received a third dose.The case-control study is based on data from a multistate hospital network and included adults ages 18 and older who were hospitalized with COVID-19 symptoms from Mar 11, 2021 through Jan 23, 2022.
Of 7,544 patients, 1,440 had lab-confirmed COVID and 6,104 controls tested negative.Patients who received two or three doses had a 90% reduced risk for ventilator treatment or death from COVID-19.
Read more on cidrap.umn.edu